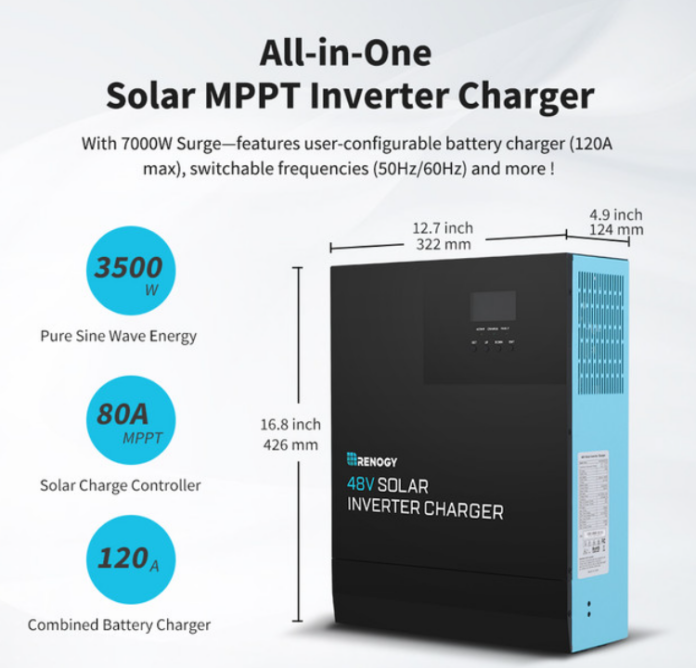
New and particularly powerful products come onto the market almost every month. Electricity storage devices with a modern three-phase hybrid inverter are now a particularly good choice.
The market for battery storage has changed significantly in the past (If you are not familiar with what is an inverter, just check this blog for details). This article will show you the advantages of such a hybrid inverter in connection with the right storage.
The difference between a hybrid inverter and an inverter
To understand the difference between a traditional power inverter for solar panels and a hybrid inverter, we first need to take a closer look at how a traditional PV inverter works. This is often referred to as the heart of a solar system, as it takes on one of the central functions.
The mini solar panels on your roof convert the sun’s rays into electricity. However, this is not the usual household alternating current (“AC”) but direct current (“DC”). For you to be able to use the solar power that your PV system generates for the electrical appliances in your household – or to feed it into the public grid, the direct current must first be converted into alternating current. This task is performed by the inverter connected to your PV system.
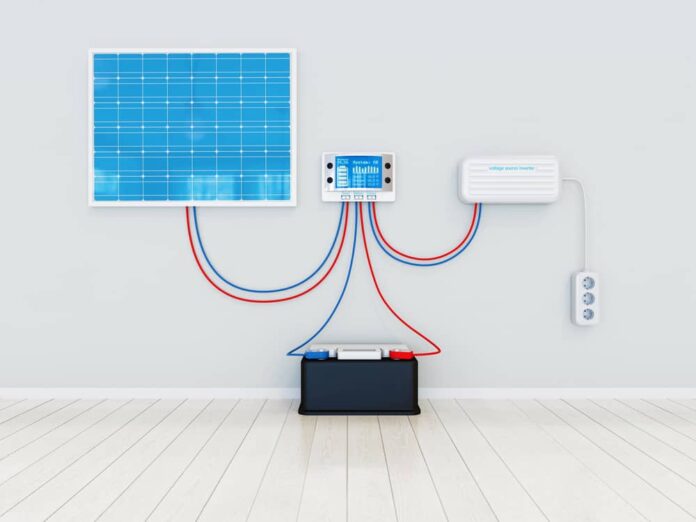
If a power storage device is to be integrated into the PV system, you need another one in addition to your PV inverter – the battery inverter. Since battery storage can only be charged with direct current, this is necessary also to convert the solar power stored in the battery into conventional household alternating current. The disadvantage of this system: there are conversion losses.
At this point, we come to the hybrid inverter. In the technology field, the term “hybrid” describes those devices that combine two or more technologies. So something is “bundled,” “mixed,” or “crossed.” The hybrid inverter thus combines the function of the PV inverter and that of the battery inverter in one device. This means that the hybrid inverter temporarily stores the excess electricity that cannot be consumed in the household during the day in the external storage system and makes it available again later.
Thus, by using a hybrid inverter, the conversion losses are minimized. You also save space and money because you no longer need a battery inverter.
In addition to the hybrid inverters, there are also so-called energy storage systems (short: ESS systems). This is a system in which the hybrid inverter is combined directly with an electricity storage device in one device. An example of an all-in-one solution of this type is the home power station from E3/DC. However, most solar solutions with a hybrid inverter connect an external power storage unit.
How does a hybrid inverter work?
A hybrid inverter is, therefore, a modern type of inverter that enables the solar power generated by the photovoltaic system to be temporarily stored with the help of a power storage unit and used at a later point in time. The hybrid inverter has a direct output to which the battery storage is connected. This means that the electricity can be loaded directly from the roof into the storage tank when it is not needed in the household and then fed into the home network later.
This saves space and is usually much easier to install, but it also means fewer losses that occur with AC-side power storage, often found on the market. Because hybrid inverters avoid double solar power conversion, the so-called conversion losses decrease significantly.
What other tasks does a hybrid inverter take on?
Therefore, the hybrid inverter’s primary task is the low-loss conversion of the direct current into the alternating current that can be used in the household. In addition, the intelligent system takes on the following additional tasks:
- Performance optimization
- Monitoring and security
- Temperature management
- Protection of functionalities
Here it becomes clear that the tasks of an inverter are as diverse as they are decisive for the yield. You should, therefore, always obtain sufficient information and advice before choosing your inverter.
Should my hybrid inverter be 3-phase or 1-phase?
Two terms frequently appear when asked about the right inverter: 3-phase and 1-phase. We explain what the terms mean and what you should pay attention to.
In general, these two types of inverters differ as follows:
1-phase: These hybrid inverters only supply power via a single phase. This means that the alternating current is delivered via a single current-carrying conductor.3-phase: In the three-phase models, on the other hand, the energy is delivered via three current-carrying conductors. You may have come across the term three-phase current, which describes this type of current flow.
The advantage of three-phase inverters is that they achieve a significantly higher nominal power and supply connected loads with electricity noticeably faster and more reliably. For this reason, 1-phase hybrid inverters are currently only very rarely installed. In addition, solar panels system with an apparent output of at least 4.6-kilovolt amperes (kVa) per phase have had to be equipped with a 3-phase inverter since 2012.
A single-phase inverter is always more economical for a small photovoltaic system. Using balancing meters, PV operators do not have to worry about power losses here.
What are the advantages of the Sungrow hybrid inverters?
The Kostal Plenticore plus and the Sungrow hybrid inverter are high-quality and reliable inverter models. The Sungrow Hybrid HV still has the edge in comparison.
On the one hand, this is because the installation and commissioning of the Sungrow models are very uncomplicated and time-saving. On the other hand, Sungrow also offers power storage and hybrid inverters. With this manufacturer, you get everything from a single source, and the components are optimally matched to each other.
In addition, Sungrow’s hybrid inverters are also suitable for larger systems with an output of up to 25 kW. Two inverters of the same size can easily be combined for this purpose.
With this intelligent two-inverter solution, up to 4 MPP trackers can also be used. As a result, up to four sides of the roof can be flexibly designed with solar modules.
The hybrid inverter system from Sungrow thus offers several advantages, especially for somewhat larger PV systems that are intended to achieve high levels of self-consumption.
Are you unsure which hybrid inverter is best suited for your project? Our specialist advisors will be happy to inform you independently about the various options.
How much does a hybrid inverter cost?
But what does it all look like from a financial perspective? Here, too, the hybrid inverter has the edge. Because you only need one instead of two inverters, some costs that would otherwise be incurred for two individual components are eliminated.
Of course, the price of a hybrid inverter always depends on the choice of manufacturer and model. For a high-quality hybrid inverter – like the ones from KOSTAL or Sungrow presented here – you can usually expect costs between 2,000 and 5,000 euros (gross).
Conclusion
The market for solar systems and electricity storage has developed rapidly. In combination with the right battery system, modern hybrid inverters make it possible to achieve higher performance at a comparable and sometimes even lower price. We briefly summarize the most important factors in terms of hybrid inverters:
If you purchase a hybrid inverter, you save both space and costs. 1-phase hybrid inverters are hardly ever used anymore since solar modules are becoming more and more powerful, and you already have 12 modules (420 Wp each). A system size comes for which single-phase inverters are not suitable. As a rule, you must reckon with costs between 2,000 and 5,000 euros (gross) for a hybrid inverter, depending on the model and the manufacturer.