Fish soup is a popular delicacy among Singaporeans. Every now and then, when consuming the soup, individuals might find a fishbone that gets stuck in the throat. Entclinic.sg encounters many such cases and it is important to be aware of the dangers of fish bone consumption. Accidents can happen and knowing an ENT clinic which can handle the situation well is paramount.
What happens when you swallow a fish bone?
Fish bones generally tend to be small and oddly shaped. Many times though it might pass through the body without any difficulty. However, it is common whereby the sharp bones can get stuck in one’s throat. The most common location of a stuck fish bones is the oesophageal sphincter.
There could be many risk factors associated with swallowing a fish bone especially if the bone is one which is more than 3 cm long. Compared to other foreign body ingestion, fish bones can cause bleeding and perforation requiring a response within the first couple of hours. If the fish bone penetrates the wall of the esophagus, this could lead to a life-threatening aortoesophageal fistula. During such an ENT emergency, it is important to visit an ENT center which is fully equipped for diagnosis and treatment with qualified hands who can put you at ease.
The most common location of the fish bone in the throat
The fish bone lodging site can vary among the young and elderly. Some individuals have a higher risk of getting food or fish bones stuck in their throat. Embedding in the oesophageal region is more common in individuals over 40 years of age. For young adults it is mostly in the oropharyngeal region. The main reason for this could be that with time there could be a deterioration in the swallowing movement and other esophageal physiological characteristics which occur with age.
The most common oropharynx sites that fish bones get lodged include the tonsils, base of the tongue, pyriform recesses and valleculae. Most of the complications occur in the places where there is physical narrowing like the upper and lower oesophageal sphincter and eminence of the aortic arch or left main bronchus. The most common lodging site however is the upper oesophageal sphincter. Fish bones which are flat in nature are embedded more often in the esophagus while linear bones lodge more in the pharynx.
How do you know if you have a fish bone in the throat?
One can often feel the fish bone in the throat as soon as it gets stuck. There is discomfort and pain in the throat, apart from this the other signs can include:
- Having a sharp pain when swallowing
- Cough
- A sensation of pricking in the throat
- An acute pain where the bone is embedded
- Blood when spitting
Home remedies before visiting the doctor.
Before visiting the doctor there are a few home remedies to try to see if the issue can be resolved. Below are five options to consider
- Having a couple tablespoons of olive oil well help lubricate the lining of your throat.
- Try to lightly chew on some bread or a banana. Coupled with the olive oil will be most effective.
- Try coughing vigorously. A forceful cough might move the lodged bone
- Try some bread followed by a cup of water
- Have some peanut butter and bread. Gulping it down will hopefully have the bone stick to the peanut butter and push it down. Chase it down with some water.
What are the procedures your ENT specialist will conduct to diagnose the fish bone?
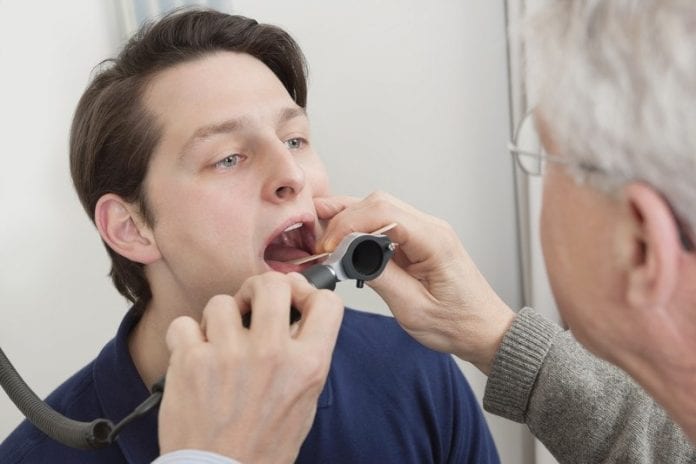

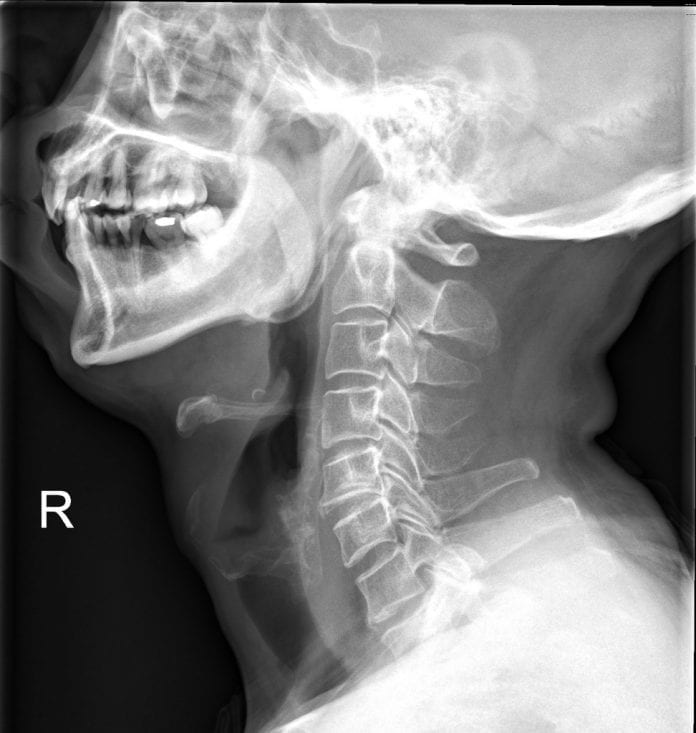
According to ENT Clinic Singapore, your otolaryngologist will do a physical examination of your oral cavity using a tongue depressor and a pen light. Then he or she may suggest plain radiography in the form of an X-rays as an initial mode of screening. However, the sensitivity of X-rays is low in the case of fish bone foreign bodies with a false negative rate of around 47%. The use of bi-plane radiography helps better compared to plain radiography. X-rays are taken in the anteroposterior view and the lateral view is important. The former however doesn’t always detect fish bones but the lateral view is good at detecting upper oesophageal and oropharyngeal lodging of fish bones.
A laryngoscope or bronchoscope too can help with detection and your ENT doctor may use one. CT scans have a high sensitivity and it’s sensitivity increases with a 3-D reconstruction, but it’s an expensive technique compared to the former methods. CT scans are a good way to find embedded foreign bodies that need focused diagnosis and treatment.
How will an ENT doctor remove your fish bone in the throat?

The mode of treatment varies with the place where the fish bone is lodged. For instance, if it is in the airway, a laryngoscope or bronchoscope, helps to view the object and remove it with special forceps. If the fish bone is in the esophagus thenan esophagoscopy needs to be done to remove it. The use of a flexible endoscope has a lower risk of perforation along with a high rate of success, but rigid endoscopes generally help in removing bones in the upper oesophageal sphincter. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is widely used as a therapeutic technique. During rare cases surgery may be needed.
Prevention tips when consuming fish?

It will go a long way in cleaning the fish properly where bones are removed prior to cooking. Fish fillets are a better choice although it might have some small bones too. Children should be well supervised when they eat bony fish and high risk individuals like the elderly and people using dentures should take small bites while eating food consciously.