Nowadays, we take many things for granted without thinking much about what it takes to make some things work. So it is with the use of devices and machines that run on electric motors. And have you ever wondered what it takes for such a drive to function? Here we come to the significance that encoders have today. In the text before you, we will explain how they work and what the differences are between them – and how do you know if an encoder is incremental or absolute?
What Are Encoders Actually And Where Are They Used?
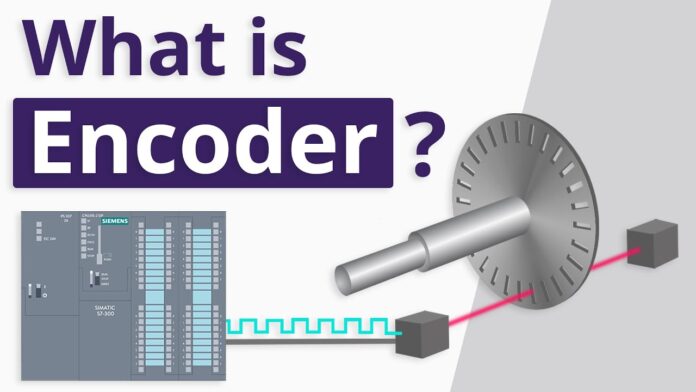
Encoders are devices that convert a mechanical into an electrical signal – so it can be suitable for further processing. They are an essential element in machines and devices with electric motor drives. We use them to measure positions, angles, speed, linear displacement, etc. Encoders are an indispensable part of any regulated electric motor drive – and their application is important in closed-loop control, especially in applications where precision control is required. The scope of encoder application is extremely large and includes most electro-mechanical devices or specialized machines in the industry, such as packer machines, elevators, cranes, etc. Encoders also find their role in specific high-tech projects of industrial automation, then robotics – as well as with large engines and generators.
What Types Of Encoders Can We Distinguish
Today, there are several types of encoders that we most often distinguish. The difference is established according to their principle of operation. Speaking of differences, the fundamental difference we make today is that between incremental and absolute encoders. Of course, this is not the only division, because we also have a different encoder according to the type of axis. In that sense, there are encoders with a full and a hollow axis. Using a hollow shaft is considered a more affordable option because it reduces installation costs and requires far less space than installing a full shaft encoder. Also, no additional mechanical equipment is required for mounting the encoder with a hollow shaft – so this option is used much more often. However, in the text, we will focus more on the primary division, which is absolute and incremental encoders. So what’s the difference?
The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders
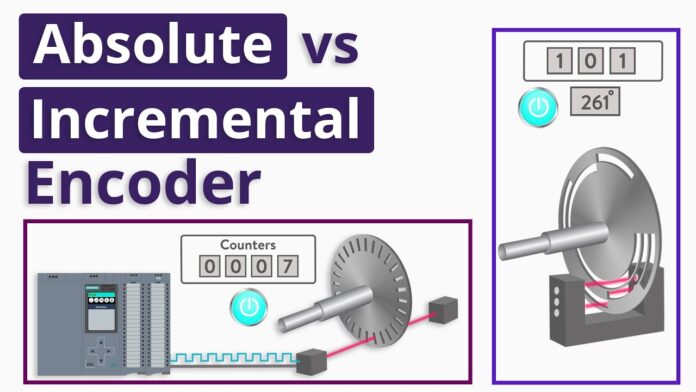
Of course, we have already pointed out that this difference is conditioned primarily by the principle on which the operation of the encoder is based. So what is the essential difference between absolute and incremental encoders? Incremental encoders are used for classic motor shaft speed counting. They are connected to the motor itself by some of the gear models. These encoders count from zero upwards – and each turn is a new number of impulses. They also have different resolutions, for example, 1000 pulses per minute. A counting element is needed to determine the speed – because the incremental encoder cannot do that. On the other hand, we have an absolute encoder which we also call a redundant encoder. According to encoder.com/absolute-encoders, such encoders are used to measure the angle of displacement – but with the memory of the last position. For example, if the device rotated 45 degrees and stayed there performing a function – the absolute encoder will remember that it stopped at a particular angle. If another 45 degrees rotation starts – the absolute encoder knows that it is currently at 90 degrees from the reference position. This is used with high-precision devices where a measurement error would be fatal.
How It Works In Practice: An Example
We will give an example of encoders used in the computer industry. Namely, with absolute encoders, the position of the motor shaft is obtained by directly reading the coded position from the disk. In this way, the error in angle detection is reduced. The detected value must be translated from binary cyclic to ordinary binary code before being brought to the processor. The incremental encoder is equipped with a transparent disk on which opaque equidistant markers are densely applied. A light detector is used to read the marker. During the rotation of the disk, the light detector generates pulses – and at each reading, displays the digital equivalent of the position increment.
Is There Another Type Of Encoder Beyond This Basic Division
Reliable information about the current position of the most common electric motor system is of great importance for many industries – from machines to the computer industry. Such control systems are very significant because of the precision that these jobs require. In addition to incremental and absolute encoders, which are the basic types – we also have hybrid ones, that represent a combination of the first two types. As we could see – the incremental systems produce an impulse for each unit of motion of a moving system. With absolute encoders, each point on the measuring axis is uniquely coded. By direct reading of the written binary code, with possible decoding – the absolute position of the moving is determined. Hybrid encoders and systems are designed to contain the best features of the previous two systems – and suppress their shortcomings.
The Significance Of Encoders
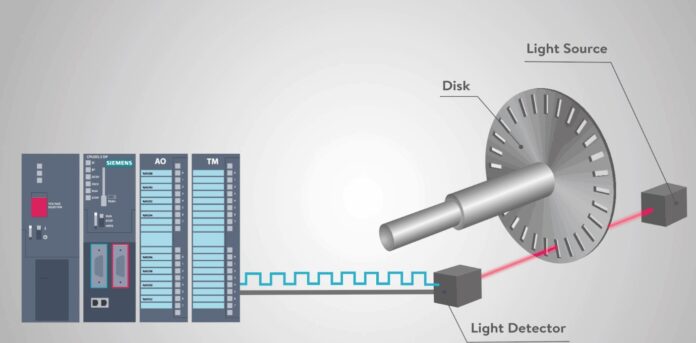
From all the above, it is clear that encoders are of great importance in various industries. Their application is pretty wide, from mechanization, through electronics, to high-precision devices. Each of these devices, which has an electric motor, must function properly. That means that encoders are necessary if we want to avoid operational errors. Encoders are here to help us detect errors, diagnose errors, record conditions, and determine current or new values of angles and positions.
The Bottom Line
While we believe that most readers have not given much thought to the principles of encoder operation. However, we hope that things are at least a bit more clear now. Today, the line between machine industry, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and informatics is thinning – and in practice, these branches often meet and overlap. We can say that encoders are one of those things that make this combination of different branches work more successfully in practice.









